84.斯皮仁诺
出处:按学科分类—医药、卫生 军事医学科学出版社《临床常用进口药物手册》第473页(13311字)
【中文释文】:
(伊曲康唑)胶囊
〔品名与结构式〕
正名:伊曲康唑胶囊
商品名:斯皮仁诺胶囊
英文名:Itraconazole Capsule
拉丁名:Capsulae Itraconazoli
分子式:C35H38Cl2N8O4
分子量:705.64
〔性状〕
本品为粉色胶囊、蓝色胶囊,内含100mg伊曲康唑丸状颗粒。
〔药代动力学〕
本品是一种合成的广谱抗真菌药,为三氮唑衍生物,对皮肤癣菌(发癣菌属、小孢霉属、絮状表皮癣菌)、酵母菌〔新型隐球菌、瓶形酵母属、假丝酵母(念珠菌)属(包括白色念珠菌、光滑念珠菌和克鲁斯念珠菌)〕、曲霉属、组织孢浆菌属、巴西副球孢子菌、申克孢子丝菌、着色霉属、支孢霉属、皮炎芽生菌以及各种其它的酵母菌和真菌感染有效。体外研究已证实本品可抑制真菌细胞膜的主要成分之一麦角固醇的合成,从而发挥抗真菌效应。
〔吸收、分布、消除〕
饭后立即服用本品,生物利用度最高。口服3~4h后血药浓度达峰值,血浆中清除呈双相性,末端相半衰期为1~1.5d,长期给药1~2周达稳定状态。在服药后3~4h,伊曲康唑稳态血药浓度分别是:0.4μl/ml(100ml每日1次),1.1μl/ml(200mg每日1次和2μl/ml(200mg每日2次)。本品血浆蛋白结合率为99.8%。全血浓度为血浆浓度的60%,在富含角蛋白的组织中,尤其是皮肤中的浓度比血浆浓度高3倍,而药物清除与表皮再生过程有关,连续用药4周后停药,7d后已测不到药物的血浆浓度,但皮肤中药物仍可保持治疗浓度达2~4周。开始治疗1周后,在甲角质中就可测到伊曲康唑,3个月疗程结束后,其药物浓度仍至少存在6个月时间,本品存在于皮脂中,汗液中也少量存在。伊曲康唑同时也集中分布在易于受到真菌感染的部位,在肺、肾脏、肝脏、骨骼、胃、脾脏和肌肉中的药物浓度比相应的血浆浓度高1~2倍,在阴道组织治疗浓度持续的时间是200mg每日1次治疗3d,可维持2d;200mg每日2次治疗1d则维持3d。本品主要在肝脏中代谢,产生大量代谢产物。其中之一是羟基伊曲康唑,体外研究发现其抗真菌活性与本品相似,生物分析法测得抗真菌药物水平约为高压液相色谱分析本品水平的2倍,经粪排泄的原型药约为所用剂量的3%~18%,以肾排泄的原型药则低于所用药剂量的0.03%,大约35%以代谢物形式在1周内经尿排泄。
〔适应证〕
斯皮仁诺适于治疗以下疾病:
妇科:外阴阴道念珠菌病。
皮肤科/眼科:花斑癣、皮肤癣菌病、真菌性角膜炎和口腔念珠菌病。由皮肤癣菌和(或)酵母菌引起的甲真菌病。
系统性真菌感染:系统性曲霉病及念珠菌病、隐球菌病(包括隐球菌性脑膜炎),组织胞浆菌病、孢子丝菌病、副球孢子菌病、芽生菌病和其它各种少见的系统性或局部真菌病。
〔禁忌证〕
禁用于对本品过敏者。
孕妇禁用。除非用于系统性真菌治疗,但仍应权衡利弊。
〔注意事项〕
1.儿科应用。因伊曲康唑用于儿童的临床资料有限,因此建议不要把伊曲康唑用于患儿,除非潜在利益优于可能出现的危害。
2.对持续用药超过1个月的病人,以及治疗过程中如出现厌食、恶心、呕吐、疲劳、腹痛或尿色加深的病人,建议检查肝功能。如果出现异常,应停止用药。
3.如果病人肝功能异常,就不应用药,除大量治疗的必要性超过肝损坏的危险性。
4.伊曲康唑绝大部分在肝脏代谢。肝硬变病人服药后的生物利用度降低。如必要服药,建议监测伊曲康唑的血浆浓度并选用适宜的剂量。
5.当发生神经系统症状时应终止治疗。
6.对肾功能不全病人,本品的口服生物利用度可能降低,建议监测本品的血浆浓度以确定适宜的剂量。
7.哺乳期妇女不宜使用,育龄妇女使用本品时应采取适当的避孕措施。
〔药物相互作用〕
1.诱酶药物如:利福平和苯妥英可明显降低本品的口服生物利用度。因此,当与诱酶药物共同服用时应监测本品的血浆浓度。
2.体外研究表明:在血浆蛋白结合方面本品与丙咪嗪、普萘洛尔(心得安)、地西泮(安定)、西咪替丁、吲哚美辛(消炎痛)、甲苯磺丁脲(甲糖宁)和磺胺二甲嘧啶之间无相互作用。
3.已报道当本品超过推荐剂量时,与环孢素A、阿司咪唑和特非那定有相互作用。环孢素A若与本品同服时,应减少剂量。
4.已报道本品与华法林和地高辛有相互作用。因此这些药物若与本品同服时,应减少剂量。
5.尚未观察到本品与AZT(齐多夫定)间的相互作用。
6.尚未观察到本品对炔雌醇和炔诺酮代谢的诱导效应。
〔用法和用量〕
为达到最佳吸收,斯皮仁诺应餐后立即给药,胶囊必须整个吞服。
表27 不同适应证应用不同的剂量用法
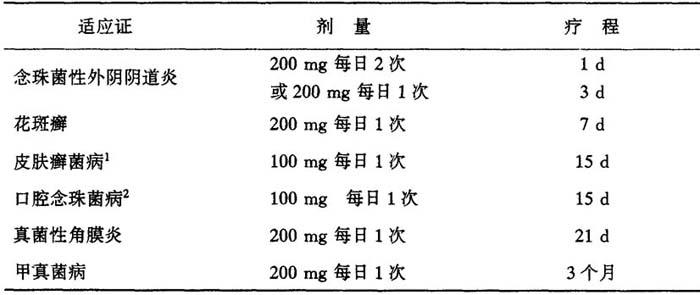
高度角化区,如足底部癣、手掌部癣需延长治疗15日,100mg/d
一些免疫缺陷病人如白血病、艾滋病或器官移植病人,伊曲康唑的口服生物利用度可能会降低,因此剂量可加倍
本品从皮肤和甲组织中清除比血浆慢,因此,对皮肤感染来说,停药后2~4周达到最理想的临床和真菌学疗效,对甲真菌来说在停药后6~9个月达到最理想的临床和真菌学疗效。
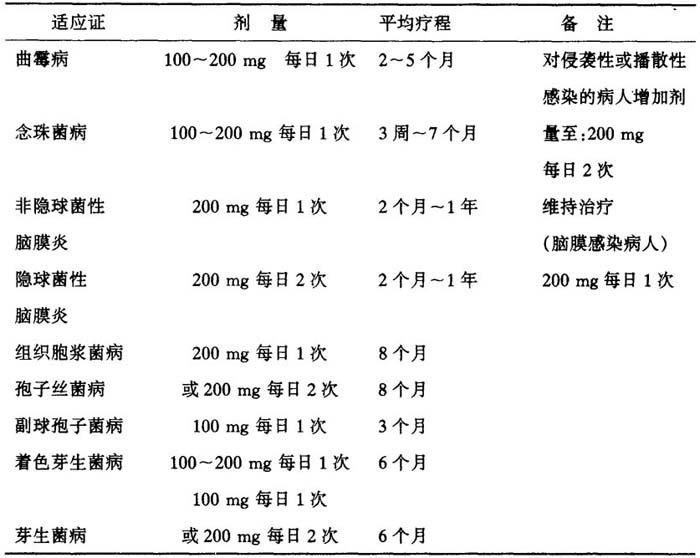
全身性真菌病:(根据不同的感染选择不同的剂量用法)。
表28 根据不同感染选择不同的剂量用法
〔副作用〕
在已报告的斯皮仁诺的副作用中常见胃肠道不适,如厌食、恶心、腹痛和便秘。其它报告较少见的副作用包括头痛、可逆性肝酶升高、月经紊乱、头晕和过敏反应(如瘙痒、红斑、风团和血管性水肿)。有个例报告出现了(重症多形红斑)综合征。
已有潜在病理改变并同时接受多种药物治疗的大多数病人,在接受斯皮仁诺长疗程治疗时可见低血钾症、水肿、肝炎和脱发等症状。有个例报告出现了外周神经病变,但是否与服用斯皮仁诺有关还不肯定。
〔过量解救〕
一旦发生,应采取支持疗法,包括洗胃;本产品能经过血液透析清除;无特殊的解毒药。
〔规格〕
100mg/粒
〔包装〕
4粒/盒或15粒/盒,铝箔水泡眼包装。
有效期:见包装盒上有效期限。
〔贮藏〕
15~30℃,存放于干燥的地方。
本品应放在儿童不能随手拿到的地方。
〔生产厂家〕
比利时贝尔瑟杨森制药有限公司
(附本品别名:依地康唑,伊康唑)
【外文释文】:
Trademark
Product name and structure
Generic name:Itraconazole capsule
Trade name:Sporanox Capsule
Latin name:Capsulae Itraconazoli
Chemical structure
Molecular formula:C35H38Cl2N8O4
Molecular weight:705.64
Properties
Pink and blue capsules,each containing 100mg itraconazole in a pellet formulation.
Pharmacodynamics
This drug is a synthetic broad-spectrum antifungal agent.It is a triazole derivative,active against infections with dermatophytes(Trichophyton spp.,Microsporum spp.,Epidermophyton floccosum),yeasts(Cryptococcus neoformans,Pityrosporum spp.,Candida spp.,including C.albicans,C.glabrata and C.krusei),Aspergillus spp.,Histoplasma spp.,Paracoccidioides brasiliensis,Sporothrix schenckii,Fonsecaea spp.,Cladosporium spp.,Blastomyces dermatitidis,and various other yeasts and fungi.
In vitro studies have demonstrated that itraconazole impairs the synthesis of ergosterol in fungal cells.Ergosterol is a vital cell membrane component in fungi.Impairment of its synthesis ultimately results in an antifungal effect.
Absorption,distribution,excretion
The oral bioavailability of itraeonazole is maximal when the capsules are taken immediately after a full meal.Peak plasma levels are reached 3-4 hours following an oral dose.Elimination from plasma is biphasic with a terminal half life of 1-1.5 days.During chronic administration,steady-state is reached after 1-2 weeks.Steady-state plasma concentrations of itraconazole 3-4 hours after drug intake are 0.4μg/ml(100mg od),1.1μg/ml(200mg od)and 2.0μg/ml(200mg bid).The plasma protein binding of itraconazole is 99.8%.Concentrations of itraconazole in whole blood are 60%of those in plasma.Uptake in keratinous tissues,especially the skin,is up to 4 times higher than in plasma,and elimination of itraconazole is related to epidermal regeneration.In contrast to the plasma levels which become undetectable within 7 days to 4 weeks after discontinuation of a 4-week treatment.Levels of itraconazole have been detected in the nail keratin as early as 1 week after start of treatment and persist for at least 6 months after the end of a 3 month course of therapy.Itraconazole is also present in sebum and to a lesser extent in sweat.Itraconazole is also extensively distributed into tissues that are prone to fungi invasion.Concentration in lung,kindey,liver,bone,stomach,spleen and muscle were found to be two to three times higher than the corresponding plasma concentration.Therapeutic levels in vaginal tissue are maintained for another 2 days after discontinuation of a 3-days course with 200mg daily,and for another 3 days after discontinuation of a 1-day course with 200mg bid.Sporanox(itraconazole)is extensively metabolized by the liver into a large number of metabolites.One of the metabolites is hydroxy-itraconazole,which has a comparable antifungal activity in vitro to itraconazole.Antifungal drug levels measured by bioassay were about 3 times those of itraconazole assayed by high performance liquid chromatography.Faecal excretion of the parent drug varies between 3-18%of the dose.Renal excretion of the parent drug is less than 0.03%of the dose,About 35%of a dose is excreted as metabolites in the urine within 1 week.
Indications
Sporanox is indicated for the treatment of following conditions:
·Gynaecological indications:vulvovaginal candidosis.
·Dermatological/ophthalmological indications:pityriasis versicolour,dermatomycosis,fungal keratitis and oral candidosis,
·Onychomycosis,caused by dermatophytes and/or yeasts.
·Systemic mycoses:systemic aspergillosis and candidosis,cryptoeoccosis
(including cryptococcal meningitis),histoplasmosis,sporotrichosis,paracoccidioidomycosis,blastomycosis,and other rarely occurring systemic or tropical mycoses.
Contraindications
·Sporanox is contraindicated in patients who have shown hypersensitivity to the drug or its excipients,
·Sporanox is contraindicated in pregnant women except for the treatment of systemic mycoses,where the potential advantages must be weighed against the potential harm to the foetus.
Warning and precautions
·Paediatric use:since clinical data of the use of itraconazole in paediatric patients is limited,it is advised that itraconazole should not be used in these patients unless the potential benefit outweighs the potential risks.
·It is advisable to monitor liver function in patients receiving continuous treatment of more than one month and in patients developing symptoms such as anorexia,nausea,vomiting,fatigue,abdominal pain or dark urine.If abnormal,treatment should be stopped.
·In patients with raised liver enzymes treatment should not be started unless the expected benefit exceeds the risk of hepatic injury.
·Itraconazole is predominantly metabolized in the liver.The oral bioavailability in cirrhotic patients is somewhat decreased.It is advised to monitor the itraconazole plasma concentrations and to adapt the dose when necessary.
·If neuropathy occurs that may be attributable to Sporanox,the treatment should be discontinued.
·In patients with renal insufficiency,the oral bioavailability of itraconazole may be lower.Monitoring of the itraconazole plasma concentrations to determine the proper dose is advisable.
·Not appropriate for breastfeeding women;women of childbearing age should take adequate contraceptive precautions when using this drug.
Interactions
·Enzyme-inducing drugs such as rifampicin and phenytoin significantly reduce the oral bioavailability of itraconazole.Consequently,monitoring of the itraconazole plasma concentrations is advised when enzyme-inducing agents are co-administered.
·In vitro studies have shown that there are no interactions on the plasma protein binding between itraconazole and imipramine,propranolol,diazepam,cimetidine,indomethacin,tolbutamide and sulfamethazine.
·At daily doses exceeding the recommended dosage of itraconazole,an interaction with cyclosporin A,astemizole and terfenadine has been documented.The dosage of cyclosporin A,if co-administered with itraconazole,should be reduced.
·An interaction with warfarin and digoxin has been reported.Therefore the dosage of these drugs,if coadministered with itraconazole,should be reduced.
·No interaction of itraconazole wiht AZT(zidovudine)has been observed.
·No inducing effects of itraconazole on the metabolism of ethinyloes tradiol and norethisterone were observed.
Dosage and administration
For optimal absorption,it is essential to administer Sporanox immediately after a full meal.
The capsules must be swallowed whole.
Table 27
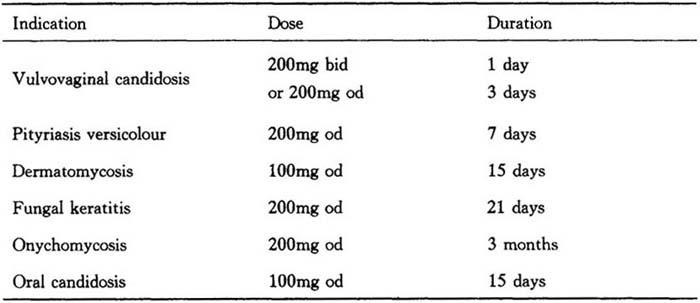
Highly keratininzed regions as in plantar tinea pedis and palmar tinea manus require an additional treatment of 15 days at100mg daily.
In some immunocompromised patients,e.g.neutropenic,AIDS or organ transplant patients,the oral bioavailability of itraconazole may be decreased.Therefore,the doses may need doubling.
Elimination of Sporanox from skin and nail tissue is slower than from plasma.Optimal clinical and mycological response is thus reached 2 to 4 weeks after the cessation of treatment for skin infections and 6 to 9 months after the cessation of treatment for nail infections.
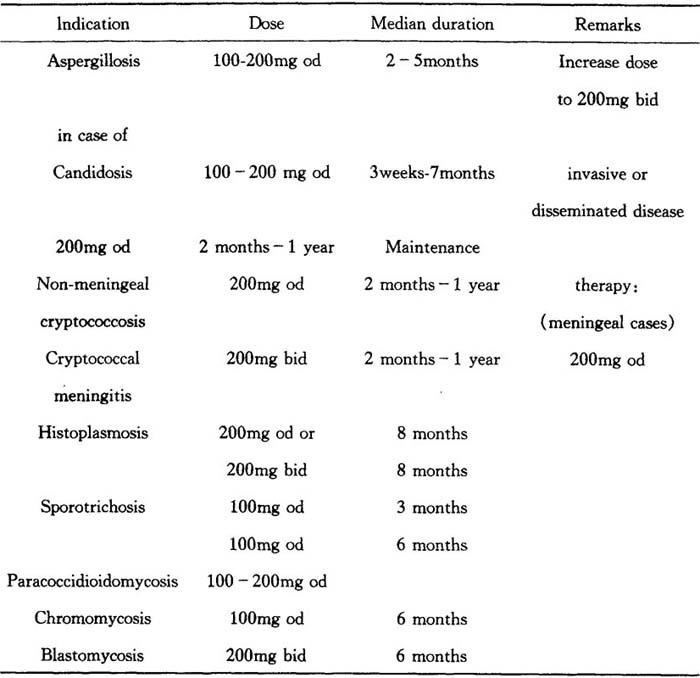
Systemic mycoses(dosage,recommendations vary according to the infection treated)
Table 28
Adverse reactions
The most frequently reported adverse experiences in association with the use of Sporanox were of gastro-intestinal origin,such as dyspepsia,nausea,abdomin pain and constipatian.Less frequently reported adverse experiences include headache,reversible increases in hepatic enzymes,menstrual disorder,dizziness and allergic reactions(such as pruritus,rash,urticaria and angiooedema).An isolated case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome has also been reported.
In patients receiving prolonged treatment,most of whom had major underlying pathology and multiple concomitant medications,cases of hypokalaemia,oedema,hepatitis and hair loss have been observed.Isolated cases of peripheral neuropathy have also been reported,but the causal association with Sporanox was uncertain.
Overdosage
In the event of overdosage,supportive measures,including gastric lavage should be employed.
Itraconazole cannot be removed by haemodialysis.
No specific antidote is available.
Specifications
100mg/capsule
Packing
4 or 15 Capsules per pack,blister packing
Expiring date:see the outside package.
Storage
15-30℃,store in a dry place.
Manufacturer
Janssen Pharmaceutica,Beerse/Belgium