56.莫敌
出处:按学科分类—医药、卫生 军事医学科学出版社《临床常用进口药物手册》第311页(16872字)
【中文释文】:
(头孢地秦)1.0/2.0
有效成分:头孢地秦
〔成分〕
莫敌1.0:每支含有1.075g头孢地秦二钠干粉,相当于1.0g头孢地秦。
莫敌2.0:每支含有2.15g头孢地秦二钠干粉,相当于2.0g头孢地秦。
〔性质〕
莫敌是一种胃肠外使用的头孢类抗生素。作为β-内酰胺类抗生素,它通过阻止细菌细胞壁的合成而发挥杀菌作用,莫敌对包括需氧菌和厌氧菌在内的多数临床上重要革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌有效。它可以抵抗大多数β-内酰胺酶而保持稳定,此酶可使许多细菌对早期青霉素类和头孢菌素产生耐药。
莫敌能够快速、广泛地分布于体液并很好地穿过组织,达到明显超过大多数病原菌最小抑菌浓度的高水平。
体外研究表明莫敌和氨基糖甙类抗生素具有协同作用。
莫敌不在体内代谢,主要通过肾脏排出。人体研究表明,治疗剂量的莫敌无肾毒性作用。
〔适应证〕
头孢地秦敏感的病原菌引起的感染。
妇女无并发症的下泌尿道感染,其它上或下泌尿道感染,下呼吸道感染,淋病。在体外,莫敌一般对下列病原菌敏感:金黄色葡萄球菌(不包括对甲氧西林耐药的菌株),肺炎链球菌,链球菌属,淋奈瑟球菌(包括产β-内酰胺酶的菌株),脑膜炎奈瑟菌,卡他布兰汉球菌,大肠埃希杆菌,志贺菌属,沙门菌属,枸橼酸杆菌属,克雷白杆菌属,普通变形菌,奇异变形菌,普鲁威登斯菌属,摩氏摩根菌,流感嗜血菌,棒杆菌属。
敏感性不同的病原菌有:类杆菌属,肠杆菌属,表皮葡萄球菌,沙雷菌属。
莫敌无效的有:假单孢菌属,不动杆菌属,粪肠球菌,李斯特菌属,支原体属以及衣原体属。
〔禁忌证〕
对头孢菌素过敏者。
〔注意事项〕
对青霉素和其它β-内酰胺类抗生素过敏的病人存在交叉过敏的可能。与氨基糖甙类药物同时使用时,必须监测肾功能(另见“药物相互作用”)。儿童中使用莫敌尚无临床经验。
妊娠期和哺乳期的使用:虽然动物试验表明对儿童没有任何致畸或毒性作用,但是在妊娠期,尤其在怀孕的最初3个月不应使用,除非有严格的指征。
哺乳期妇女无使用莫敌的资料。由于尚不了解此药的有效成分是否通过乳汁排泌,所以哺乳期妇女不应使用莫敌。
〔不良反应〕
过敏反应:可能出现皮肤过敏反应(荨麻疹);药物热;严重的急性过敏反应(过敏症,有时可发展为危及生命的休克),此时需要紧急治疗(见下文的推荐处理措施)。对胃肠道的影响:恶心,呕吐和腹泻。在治疗过程中治疗及治疗后最初几周内,病人出现严重、持续性腹泻应考虑有伪膜性肠炎的可能,这种抗生素治疗所致的肠道炎症状态可能会危及生命。在这种情况下应立即停用莫敌,医师必须马上采取适当的治疗,抑制肠道运动的药物对这种病人禁止使用。
对肝功能的影响:血清肝酶(SGOT,SGPT,rGT,碱性磷酸酶,LDH)及胆红素升高。
血液成分的改变:血小板计数减少(血小板减少症);嗜酸性细胞计数增加(嗜酸性细胞增多症);极少见的溶血性贫血。和其它β-内酰胺类抗生素相同,在使用莫敌过程中,特别是在长期使用时,可能发生白细胞减少及少见的粒细胞缺乏症,当疗程超过10d时,应监测血像。
肾脏:少数情况下,可见反映肾功能受损的血清肌酐和尿素的暂时性升高,在使用头孢菌素治疗过程中,间质性肾炎的发生非常少见。在使用莫敌治疗时有急性肾衰的个案报道,但由于此类病例大多同时具有其它可能的病因,所以二者之间尚无明确的因果关系。
局部反应:注射部位的炎症反应和疼痛。
同其它抗生素一样,应用莫敌,特别是长期使用,会导致不敏感微生物的过度生长。对于病人病情的反复评价是很必要的,如果治疗中出现双重感染,应该采取适当的措施。
〔药物相互作用〕
与丙磺舒合用时可延迟莫敌的排泄。
病人同时或随后使用具有潜在肾毒性的药物,如氨基糖甙类,二性霉素B,环孢素,顺铂,万古霉素,多粘菌素B或粘菌素,应密切监测肾功能,因为这些药物的毒性作用可被加强。
使用强效利尿剂,如呋塞米(速尿)的病人,大剂量的头孢菌素治疗可以引起肾功能的损伤,但这不会发生于莫敌的推荐剂量。
在莫敌治疗过程中,少数病例可以发生Coombs实验假阳性结果,非酶法测定尿糖也可能出现假阳性结果,因此在莫敌治疗过程中应使用酶法测定尿糖。
〔剂量〕
用药的剂量、方式取决于感染的严重程度、病原菌的敏感性以及病人的情况。除非另遵医嘱,成人及青少年使用下述剂量:
表19 莫敌的用药剂量
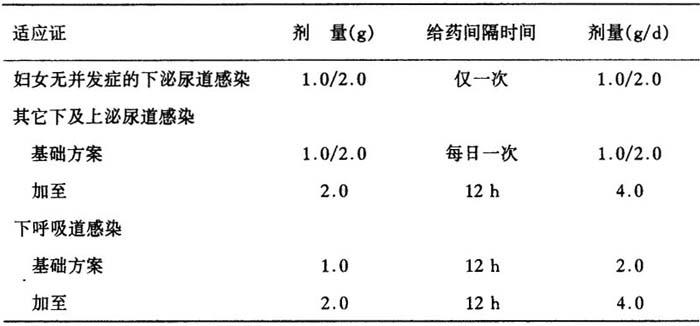
单剂量莫敌0.25g或莫敌0.5g可用于治疗淋病。肾功能受损病人莫敌的首次剂量与肾功能正常者相同,进一步治疗应按下述减量:
表20 肾功能受损病人的用药剂量

根据血清肌酐水平,由下列公式(Cockcroft公式)可计算出肌酐清除率:
男性:
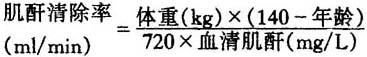
女性:
上述公式结果乘以0.85。
血液透析病人:0.5/1.0g莫敌,透析当天使用。莫敌必须在透析后给药。
〔用药方法〕
静脉注射:1支莫敌1.0溶于4ml或莫敌2.0溶于10ml注射用水,于3~5min内注射。
静脉输注:若需要,莫敌可以短时间内静脉输注。每支莫敌1.0或2.0溶于40ml注射用水、生理盐水或林格液中,20~30min输注。
在5%或10%葡萄糖溶液中,莫敌只能短时间保持稳定,所以此溶液必须立即输注。
莫敌不易溶于乳酸钠溶液。
尚无与其他输注溶液的配伍性研究。
莫敌不能与其它抗生素在同一注射器或其它输注溶液内混合,这对于上文所述氨基糖甙类同样适用。
肌肉注射:1支莫敌1.0溶于4ml或莫敌2.0溶于10ml注射用水中,注入臀肌深部,肌肉注射产生的疼痛可通过莫敌溶于相当的1%利多卡因液中而防止,在这种情况下,必须严格避免注入血管内。
莫敌液在配制后应尽早使用,室温下保存不超过6h,在2~8℃冰箱中不得超过24h。
联合治疗:如果怀疑合并有假单胞菌属的混合感染,莫敌可以与氨基糖甙类合用,但这两种药必须分开给药。
疗程:根据病人的反应确定疗程。
对妇女无合并症的急性下泌尿道感染,单剂量的莫敌通常已足够。
对于呼吸道感染,一般疗程为10~14d,有时可长一些。
体温降至正常及症状控制后,还应继续治疗至少3d。
〔贮存〕
避光、避热保存。
〔有效期〕
有效期过后请勿使用。
药品应保存在儿童难以触及的地方。
〔过敏性休克发生时的急救措施〕
一般推荐以下急救措施:在早期表现(出汗、恶心、紫绀)出现时,立即停止注射,保留静脉管或重新静脉插管。除了通常的急救措施外,保持病人卧位,双腿抬高,气道通畅。
紧急药物治疗
1.静脉注射肾上腺素包括以下步骤将市售1:1000肾上腺素1ml稀释至10ml,第一步缓慢注射1ml此稀释液(相当于0.1mg肾上腺素),同时监测脉搏和血压(观察心律紊乱),如果需要可以重复注射。
2.糖皮质激素静脉注射如250~1000mg甲泼尼龙,必要时可重复给药。
以上推荐剂量适于正常体重的成年人。在儿童,剂量应根据体重减量。
3.静脉注射容量代用品如血浆扩充剂,人血白蛋白,平衡电解质溶液。
其它治疗措施:如人工呼吸,氧气吸入,抗组胺药物。
〔包装〕
莫敌1.0:1支装,每支1.075g干粉,带或不带4ml安瓿注射用水;5支装,每支1.075g干粉,带或不带5支4ml安瓿注射用水。
莫敌2.0:1支装,每支2.15g干粉,带或不带注射用水;5支装,每支2.15g干粉,带或不带5支10ml或40ml注射用水。另有莫敌0.25,莫敌0.5提供。
〔生产厂家〕
德国美因河畔法兰克福赫斯特公司
(附本品别名:莫敌威,Timcef)
【外文释文】:
Active ingredient:Cefodizime disodium
Composition
Modivid 1.0:each vial contains 1.075 g cefodizime disodium,as dry substance,corresponding to 1.0 g cefodizime.
Modivid 2.0:each vial contains 2.15 g cefodizime disodium,as dry substance,corresponding to 2.0 g cefodizime.
Properties
Modivid is a cephaolsporin antibiotic for parenteral use.As a beta-lactam antibiotic,it acts bactericidally by preventing cell-wall synthesis in bacteria.Modivid is effective against numerous clinically significant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria,including both aerobes and anaerobes.It is stable against the action of most beta-lactamases,the enzymes which have enabled many bacteria to develop resistance to the earlier penicillins and cephalosporins.
Modivid is rapidly and widely distrubuted in body fluids and penetrates tissues very well,reaching high levels which clearly exceed the minimum inhibitory concentrations for most pathogens.
In vitro studies on combinations of Modivid and aminoglycoside antibiotics showed synergistic effects.
Modivid is not metabolized and is excreted mainly via the kidney.Studies in humans with therapeutic doses have shown no nephrotoxic effects.
Indications
Infections caused by cefodizime-sensitive pathogens.
Uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in women,other lower and upper urinary tract infections,lower respiratory tract infections,gonorrhoea.
Modivid is generally effective in vitro against the following pathogens:Staphylococcus aureus(except methicillin-resistant strains),Streptococcus pneumoniae,Streptococcus spp,Neisseria gonorrhoeae(including beta-lactamase-producing strains),Neisseria meningitidis,Branhamella catarrhalis,Escherichia coli,Shigella spp,Salmonella spp,Citrobacter spp,Klebsiella spp,Proteus vulgaris,Proteus mirabilis,Providencia spp,Morganella morganii,Haemophilus influenzae,and Corynebacterium spp.
Pathogens with varying susceptibility are:Bacteroides spp,Enterobacter spp,Staphylococcus epidermidis,Serratia.
Modivid is not effective against:Pseudomonas spp,Acinetobacter spp,Enterococcus faecalis,Listeria,Mycoplasma,and Chlamydia.
Contraindications
HypersensItivity to cephalosporins.
Precautions
The possibility of cross-sensitivity exists in patients hypersensitive to penicillins or other beta-lactam antibiotics.
Renal function must be monitored in patients treated concomitantly with aminoglycosides(see also Interactions).
There is no clinical experience of the use of Modivid in children.
Use in pregnancy and lactation:although animal experiments did not reveal any malformation or toxic effect on the foetus,Modivid should not be used during pregnancy,especially in the first three months,unless strictly indicated.
There is no information on the use of Modivid in nursing mothers.Since it is unknown whether the active ingredient is excreted in mother’s milk,Modivid should not be used in nursing mothers.
Adverse reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions:allergic skin reactions with urticaria(nettle rash);drug fecer,severe acute allergic reactions(anaphylaxis,sometimes progressing to life-threatening shock)may occur and require emergency treatment(see recommended measures below).
Effects on the gastrointestinal tract:nausea and vomiting,diarrhoea.The possibility of pseudomembranous colitis should be considered in patients in whom severe,persistent diarrhoea occurs during treatmen or in the initial weeks thereafter.This intestinal inflammatory condition induced by antibiotic therapy may be life-threatening.Administration of Modivid is to be halted immediately in such circumstances.The doctor must initiate appropriate treatment without delay.Drugs that inhibit intestinal motility(peristalsis)must not be taken in such cases.
Effects on liver function:rise in serum liver enzymes(e.g.SGOT,SGPT,gamma-GT,alkaline phosphatase,LDH)and bilirubin.
Changes in blood constituents:Decreased platelet count(thrombocytopenia);increased eosinophil count(eosinophilia);very rarely,haemolytic anaemia.As with other beta-lactam antibiotics,leucopenia and,more rarely,agranulocytosis may develop during treatment with Modivid,particularly if given over long periods.For courses of treatment lasting longer than 10 days,the blood count should therefore be monitored.Kidney:temporary rises in serum creatinine and urea,indicating impairment of renal function,may occur in rare instances.More rarely,cases of interstitial nephritis have been observed during treatment with cephalosporins.In isolated cases,acute renal failure has been reported during treatment with Modivid as well,but a clear-cut causal relationship could not be established,since in most of these cases other possible causes existed at the same time.
Local reactions:inflammatory irritation and pain at the site of injection.
As with other antibiotics,the use of Modivid,especially if prolonged,may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms.Repeated evaluation of the patient’s condition is essential.If superinfection occurs during therapy,appropriate measures should be taken.
Interactions
Concomitant use of probenecid prolongs the excretion of Modivid.
Patients under concurrent or subsequent medication with potentially nephrotoxic drugs,e.g.aminoglycosides,amphotericin B,cyclosporin,cisplatin,vancomycin,polymyxin B or colistin,should be closely monitored for renal function,because their nephrotoxic effect may be potentiated.
In patients under treatment with potent diuretics,such as furosemide,high-dose treatment with cephalosporins may result in impairment of renal function.This is improbable with the doses recommended for Modivid.
A false-positive result for the Coombs’test may be obtained in rare cases during treatment with Modivid.Non-enzymatic methods for the determination of glycosuria may also give a false-positive result.Glycosuria should be determined by enzymatic methods during Modivid treatment.
Dosage
Dosage and mode of administration depend on the severity of the infection,sensitivity of the pathogen,and condition of the patient.Unless otherwise prescribed,the following doses are used in adults and adolescents:
Table 19
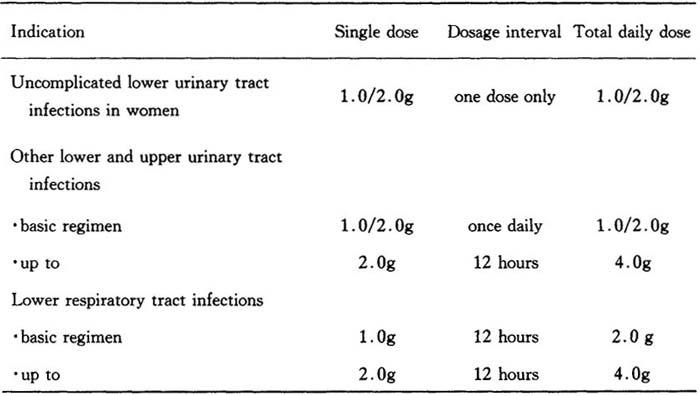
Gonorrhoea is to be treated with single doses of Modivid 0.25 or Modivid 0.5.
Dosage in patients with impaired renal function:the first dose of Modivid in patients with impaired renal function is the same as in normal renal function.For further treatment,
the dose should be reduced as follows:
Table 20

Based on the serum creatinine level,creatinine clearance can be calculated using the following formula(Cockcroft’s equations):
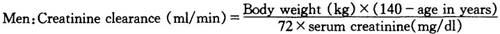
Women:Multiply the product of the above equation by 0.85.
Haemodialysis:0.5/1.0 g Modivid;on dialysis days,Modivid must be given after dialysis.
Administration
Intravenous injection:the contents of 1 vial of Modivid 1.0 are dissolved in 4 ml or Modivid 2.0 in 10 ml water for injection,and then injected over a period of 3-5 minutes.
Intravenous infustion:if required,Modivid may be administered by short intravenous infusion.The contents of 1 vial of Modivid 1.0 or 2.0 are dissolved in 40 ml water for injections,in normal saline,or in Ringer’s solution,and then infused over 20-30 minutes.
Modivid remains stable for only a short period of time in 5%or 10%glucose solution,such a solution should therefore,be infused immediately.
Modivid is not miscible with sodium lactate solution.
The compatibility with other infusion solutions has not been studied.
Modivid should not be mixed with other antibiotics in the same syrine or with other infusion solutions;this applies above all to aminoglycosides.
Intramuscular injection:the contents of 1 vial of Modivid 1.0 are dissolved in 4 ml or Modivid 2.0 in 10 ml water for injections,and then injected deep into the gluteus muscle.Pain resulting form the im injection can be prevented by dissolving Modivid in the corresponding amount of 1%lidocaine solution,but in this case intravascular injection must be strictly avoided.
Modivid solutions should be used as soon as possible after reconstitution.They must not be stored at room temperature for longer than 6 hours,or for longer than 24 hours in a refrigerator at 2-8℃。
Combination therapy:if mixed infections with Pseudomonas are suspected,Modivid may be administered in combination with an aminoglycoside.The two preparations must be administered separately.
Duration of treatment:the duration of treatment depends on the patient’s response.
One single dose of Modivid is usually adequate for the treatment of acute uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in women.
In respiratory tract infections,the usual duration of treatment is 10-14 days and occasionally longer.
Treatment must be continued for at least three days after the body temperaure has returned to normal and symptoms have subsided.
Storage
Protect from light and heat.
Expiry date
Do not use later than the date of expiry.
Keep medicines out of the reach of children!
Emergency measures to be taken in the event of anaphylactic shock
Generally,the following emergency procedure is recommended:at the first signs(sweating,nausea,cyanosis),interrupt the injection immediately,but leave the venous cannula in place or perform venous cannulation.In addition to the usual emergency measures,ensure that the patient remains lying,with the legs raised and airways patent.
Emergency drug therapy
Immediately epinephrine(adrenaline)iv:dilute1 ml of commercially available epinephrine solution 1∶1 000 to 10 ml.In the first instance,slowly inject 1 ml of this dilution(equivalent to 0.1 mg epinephrine)while monitoring pulse and blood pressure(watch for disturbances in cardiac rhythm).Repeat as required.
Then glucocorticoids iv,e.g.250-1 000 mg methylprednisolone.Repeat as required.
The dosage recommendations refer to adults of normal weight.In children,the reduction of dose should be in relation to body weight.Subsequently volume substitution iv,e.g.plasma expanders,human albumin,balanced electrolyte solution.
Other therapeutic measures,e.g.artificial respiration,oxygen inhalation,antihistaminics.
Presentation
Modivid 1.0
1 vial of 1.075 g dry substance,with or without ampoule of 4 ml water for injections.
5 vials each of 1.075 g dry substance,with or without 5 ampoules of 4 ml water for injections
Modivid 2.0
1 vial of 2.15 g dry substance,with or without water for injections.
5 vials each of 2.15 g dry substance,with or without 5 ampoules of 10 ml or 5 vials of 40 ml water for injections.
Also available:Modivid 0.25,Modivid 0.5
Manufacturer
Hoechst AG D-65926 Frankfurt am Main Germany