10.头孢三嗪
出处:按学科分类—医药、卫生 军事医学科学出版社《临床常用进口药物手册》第34页(15619字)
【中文释文】:
肌肉/静脉注射剂
(灭菌头孢三嗪钠注射剂U.S.P.)
本品为半合成的第三代头孢菌素,其化学式为C18H16N8Na2O7S33.5H2O。
〔成分及规格〕
头孢三嗪-0.25g
每支含与250mg头孢三嗪等价的灭菌头孢三嗪钠
头孢三嗪-0.5g
每支含与500mg头孢三嗪等价的灭菌头孢三嗪钠
头孢三嗪-1.0g
每支含与1000mg头孢三嗪等价的灭菌头孢三嗪钠
包装:
头孢三嗪0.25g和0.5g
每支含与0.25g或0.5g头孢三嗪等价的干物质,并有一支含5ml灭菌注射用水的
安瓿头孢三嗪1.0g
每支含与1g头孢三嗪等价的干物质,并有1支含10ml灭菌注射用水的安瓿
〔临床药理学〕
肌肉注射相当于0.5g及1.0g的头孢三嗪,据报告在2h后血浆中平均峰浓度分别达43μg/ml及80μg/ml,有85%~95%的药物与血浆蛋白结合。头孢三嗪的消除半衰期在6~9h间,初生儿则更长。
静脉注射相当于0.5g及1.0g头孢三嗪,据报告大约在给药0.5h后血浆平均峰浓度分别为82μg/ml及151μg/ml.。
头孢三嗪广泛分布于组织及体液中,它透过胎盘并以低的浓度分泌到乳汁中。当脑膜发炎时,在脑脊液中亦能达到治疗浓度。
约有40%~65%的头孢三嗪以原型主要经肾小球过滤由尿中排出,其余的经胆排出。最终大便中发现的已是无微生物活性的化合物。
与健康的成年人相比,头孢三嗪的药代动力学在老年人及有肝或肾功能不全病人中仅有极轻微的改变。因此,对上述病人,即使头孢三嗪的用量高达2g/d,通常也不必调整剂量。
〔抗菌活性〕
头孢三嗪是杀菌药,通过抑制细胞壁的合成而起作用。
头孢三嗪对革兰阴性菌及革兰阳性菌产生的β-内酰胺酶(青霉素酶及头孢菌素酶)有高度的稳定性。头孢三嗪的活性谱在体外通常包括下列微生物:
1.革兰阳性菌 金黄色葡萄球菌(包括产生青霉素酶的菌株)、表皮葡萄球菌、酿脓链球菌(A组β-溶血链球菌)、无乳链球菌(B组链球菌)、肺炎链球菌。
(注:能耐甲氧苯青霉素的葡萄球菌亦能耐头孢菌素包括头孢三嗪。大多数的肠球菌,粪链球菌及D组链球菌等菌株亦能耐头孢三嗪。)
2.革兰阴性菌 产气肠杆菌、大肠杆菌、阴沟肠杆菌、流感嗜血杆菌(包括耐氨苄青霉素抗性的菌株),副流感嗜血杆菌、克雷白菌(包括肺炎克氏杆菌)、淋球菌(包括产生和不产生青霉素酶的菌株),脑膜炎双球菌、奇异变形杆菌、普通变形杆菌、摩氏摩根尼拉菌、粘质沙雷菌(上列微生物能多重耐其他抗生素类如青霉素,头孢菌素,氨基甙类等的许多菌株都对头孢三嗪敏感)。
绿脓杆菌的许多菌株,弗氏枸椽菌、迪氏枸椽菌、普罗维登斯菌属(包括里氏普罗维登斯菌),沙门菌(包括伤寒杆菌),志贺菌,醋酸钙不动杆菌等。
头孢三嗪在体外对拟杆菌属及梭状芽胞杆菌属也有活性(难辨梭状芽胞杆菌许多菌株是耐药的)。
〔适应证〕
下呼吸道感染,尿道感染,骨盆腔炎症,非并发性淋病,皮肤及软组织感染,细菌性败血病,骨及关节感染,脑膜炎,预防手术感染。
〔剂量〕
头孢三嗪通常剂量为1~2g/d(肌肉注射/静脉注射),一次给药或分为等分,每日二次给予,视感染的类型及严重性而定。总剂量不得超过4g/d。
头孢三嗪治疗在感染的病征及症状消失后一般至少持续2d。通常疗程为4~14d。并发感染时需更长时间的治疗。对非并发的淋病感染,头孢三嗪0.25g单剂肌肉注射。
预防手术感染:头孢三嗪1g手术前0.5~2h前给予。治疗由绿脓杆菌引起之感染,疗程至少要持续10d。肝或肾功能不全的病人,不必调整剂量,但有严重肾功能不全的病人(如透析的病人)及兼有肝、肾功能不全的病人应监测血中水平。
儿童:治疗儿童严重感染,除脑膜炎外,建议剂量为50~75mg/(kg·d)(不得超过2g),将剂量分为二,每隔12h给药1次。
脑膜炎:剂量100mg/(kg·d)(不得超过4g)分次给予,每隔12h一次。
〔副作用〕
人对头孢三嗪通常耐受性良好,有报道的副作用包括:胃肠道紊乱(腹泻,恶心,呕吐),局部反应(注射部位疼痛、硬结或触痛,静脉注射后罕见出现静脉炎),过敏(皮疹,罕见瘙痒,发热或寒战),血液学紊乱(嗜酸细胞增多,血小板增多,白细胞减少、罕见有贫血、中性白细胞减少、淋巴细胞减少、血小板减少及凝血酶原时间延长)、肝功能紊乱(SGOT,SGPT升高,罕见者有碱性磷酸酯酶及胆红素升高),肾脏(血尿素氮升高及肌酐异常升高),头痛,头晕,女性阴道炎及潮红。
其他罕见的反应包括白细胞增多、淋巴细胞增多、嗜碱细胞增多、黄疸、糖尿、血尿、过敏反应、支气管痉挛、血清病、腹痛、结肠炎、腹胀、心悸、鼻出血等。
〔注意事项〕
肝功能不全病人的剂量不必调整,但对同时有肝功能不全和明显的肾病病人,未密切监测血清浓度时头孢三嗪剂量应不超过2g/d。
维生素K合成不良或贮量不足的病人(如慢性肝病及营养不良)用头孢三嗪治疗时应监测凝血酶原时间。如果在治疗前或治疗期间凝血酶原时间延长,就要补给维生素K(每周10mg)。
长期使用头孢三嗪可造成不敏感微生物过度生长。
动物研究并未发现致畸作用,但孕妇应用并不适宜,只有在确有必要时方可给孕妇使用本品。
头孢三嗪以低浓度分泌到乳汁中,因而哺乳妇女用药宜小心。
〔警告及禁忌证〕
对青霉素敏感的病人使用头孢三嗪要谨慎。
当病人出现有可疑为胆囊疾病的征兆或症状且考虑保守治疗时,为谨慎起见应予停药。已知对头孢菌素类药物过敏的病人禁用头孢三嗪。
〔给药方式〕
注射剂成品有三种规格:0.25g,0.5g及1.0g。而每种又分为供肌肉注射及静脉注射用的不同包装。肌肉注射用的稀释剂为1%(w/v)的盐酸利多卡因溶液,而静脉注射用的稀释剂为无菌注射用水。建议使用新鲜配制的溶液。
配制方法如下:
肌肉注射液:头孢三嗪0.25g或0.5g溶于2ml,头孢三嗪1.0g溶于3.5m1的1%(w/v)盐酸利多卡因溶液,作深部臀部肌肉注射。建议每侧注射不要超过1.0g。利多卡因溶液绝不可用作静脉注射。
静脉注射液:头孢三嗪0.25g或0.5g溶于5ml,头孢三嗪1.0g溶于10ml无菌注射用水中。以2~4min的时间慢慢注入静脉中。
〔配伍及稳定性〕
溶解后,不需要避光贮存。
由于溶剂、溶液浓度及贮存时间的不同,溶液会呈显由浅黄色到琥珀色等不同颜色。
下表中用于肌肉注射的头孢三嗪溶液在表中所提供的条件下,贮存相应时间,药效稳定(药效损失小于10%)。
表2 用于肌肉注射的头孢三嗪溶液在不同条件下的稳定性

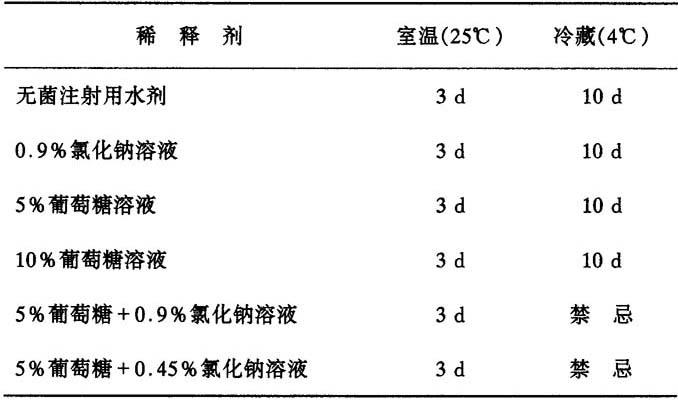
静脉注射浓度为10mg/ml、20mg/ml及40mg/ml头孢三嗪溶液,贮存在玻璃或者PVC塑料容器中,经过下表所列时间,性质仍然是稳定的。
表3 用于静脉注射的头孢三嗪溶液在不同条件下的稳定性
〔生产厂家〕
印度
(附本品别名:菌必治、抗菌治、头孢曲松、菌得治、菌必灭、罗氏芬、头孢泰克松、Rocephin、Ro13-9904)。
【外文释文】:
(Sterile Ceftriaxone Sodium U.S.P.)
Cefaxone(sterile Ceftriaxone Sodium U.S.P.)is a semisynthetic third generation Cephalosporin.Its chemical formula is Ct8H16N8Na2O7S33.5H2O
Composition and presentation
CEFAXONE-0.25g
Each vial contains Sterile Ceftriaxone Sodium U.S.P.equivalent to Ceftriaxone 250 mg
CEFAXONE-0.5g
Each vial contains Sterile Ceftriaxone Sodium U.S.P.equivalent to Ceftriaxone 500 mg
CEFAXONE-1.0g
Each vial contains Sterile Ceftriaxone Sodium U.S.P.equivalent to Ceftriaxone 1000 mg
Presentations
Cefaxone 0.25g.& 0.5g.
(1)Vial with dry substance equivalent to 0.25 g or 0.5 g Ceftriaxone and 1 ampoule containing 5 ml of sterile water for injection I.P.
Cefaxone 1.0 g.
(2)Vial with dry substance equivalent to 1 g Ceftriaxone and 1 ampoule containing 10 ml of sterile water for injection I.P.
Clinical pharmacology
After intramuscular injection of the equivalent of 0.5 g and 1.0 g of Ceftriaxone,mean peak plasma concentrations of about 43 and 80 μg/ml respectively have been reported after about 2 hours.85%-95%of the drug is bound to plasma proteins.The elimination half.life of Ceftriaxone varies between 6-9 hours,it is prolonged in neonates.
After intravenous injection of the equivalent of 0.5 g and 1.0 g of Ceftriaxone,mean peak plasma concentrations of about 82 μg/ml and 151 μg/rnl respectively have been reported after about half an hour post dosing.
Ceftriaxone is widely distributed in body tissues and fluids.It diffuses across the placenta and is excreted in breast milk in low concentrations.Therapeutic concentrations have been achieved in the cerebrospinal fluid when the meninges are inflammed.
About 40%-65% of a dose of Ceftriaxone is excreted unchanged in the urine mainly by glomerular filtration;the remainder is excreted in the bile and is ultimately found in the faeces as microbiologically inactive compounds.
Compared to that in healthy adult subjects,the pharmacokinetics of Ceftriaxone were only minimally altered in elderly subjects and in patients with renal impairment or hepatic dysfunction,hence it is usually not necessary to adjust dosage in such patients when Ceftriaxone is used in the dosages up to 2 g/d.
Antibacterial activity
Ceftriaxone is bactericidal and acts by inhibition of cell wall synthesis.Ceftriaxone has a high degree of stability in the presence of beta-lactamases(both penicillinases and cephalosporinases)of Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria.Spectrum of activity of Ceftriaxone in vitro usually includes the following micro-organisms.
Gram positive bacteria:
Staphylococcus aureus(including penicillinase producing strains)
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus pyogenes(Group A beta-haemolytic streptococci)
Streptococcus agalactiae(Group B streptococci)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
(Note Methicillin resistant staphylococci are resistant to Cephalosporins,including Ceftriaxone.Most strains of enterococci,streptococcus faecalis and Group D streptococci are also resistant to Ceftriaxone).
Gram negative bacteria:
Enterobacter aerogenes
Enterobacter cloacae
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae(including ampicillin resistant strains)
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Klebsiella species(including Klebsiella pneumoniae)
Neisseria gonorrhoeae(including penicillinase and non-penicillinase producing strains)
Neisseria meningitidis
Proteus mirabilis
Proteus vulgaris
Morganelia morganii
Serratia marcescens
(Many strains of the above organisms that are multi-resistant to other antibiotics e.g.Penicillins Cephalosporins and Aminogly cosides,are susceptible to Ceftriaxone).
Many strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Citrobacter freundii
Citrobacter diversus
Providencia species(including Providencia rettgeri)
Salmonella species(including S.typhi)
Shigella species
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus
Ceftriaxone also shows an activity in vitro against Bacteroides species and Clostridium species(most strains of C.difficile are resistant)
Indications
·Lower respiratory tract infections
·Urinary tract infections
·Pelvic inflammatory disease
·Uncomplicated gonorrhoea
·Skin and skin structure infections
·Bacterial septicemia
·Bone and joint infections
·Meningitis
·Surgical prophylaxis
Dosage
Usual daily dose of CEFAXONE is 1-2 g(i.m./i.v.)administered once a day(or in equally divided doses twice a day)depending on the type and severity of the infection.The total daily dose should not exceed 4 g.
CEFAXONE:therapy should generally be continued for at least 2 days after the signs and symptoms of infection have disappeared.The usual duration is 4-14 days;in complicated infections longer therapy may be required.
Uncomplicated gonococcal infections:CEFAXONE 0.25g i.m.as a single dose.
Surgical prophylaxis CEFAXONE 1g 0.5-2 hours before surgery.
While treating infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes,the therapy should be continued for at least 10 days.No dosage adjustement is necessary for patients with impairment of renal or hepatic function;however,blood levels should be monitored in patients with severe renal impairment(e.g.dialysis patients)and in patients with both renal and hepatic dysfunctions.
Children.For the treatment of serious infections in children,other than meningitis,the recommended total daily dose is 50-75 mg/kg.(not exceeding 2 g.)given in divided doses every 12 hours.
Meningitis.A daily dose of 100 mg/kg(not exceeding 4 g),given in divided doses every 12 hours,should be administered with or without a loading dose of 75 mg/kg.
Side effects
CEFAXONE is usually well tolerated.The side effects reported include gastrointestinal disturbances(diarrhoea,nausea,vomiting),local reactions(pain,induration or tenderness at the site of injection and rarely phlebitis after i.v.administration)hypersensitivity(rash,rarely pruritus,fever or chills),haematologic disturbances(eosinophilia,thrombocytosis and leucopenia,rarely anaemia,neutropenia,lymphopenia,thrombocytopenia and prolongation of prothrombin time),hepatic disturbances(elevations of SGOT,SGPT and rarely evlevations of alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin),renal(elevations of BUN and uncommonly elevations of creatinine)Headache,dizziness,vaginitis in females and flushing have also been reported.
Other rarely observed reactions may include leucocytosis,lymphocytosis,basophilia,jaundice,glycosuria,heamaturia,anaphylaxis,bronchospasm,serum sickness,abdominal pain,colitis,flatulence,palpitations and epistaxis.
Precautions
Dosage adjustments should not be necessary in patients with hepatic dysfunction;however,in patients with both hepatic dysfunction and significant renal disease.Ceftriaxone dosage should not exceed 2 g daily without close monitoring of serum concentrations.
Patients with impaired Vitamin K synthesis or low Vitamin K stores(e.g.chronic hepatic disease and malnutrition)may require monitoring of prothrombin time during Ceftriaxone therapy.Vitamin K administration(10 mg weekly)may be necessary if the prothrombin time is prolonged before or during therapy.
Prolonged use of Ceftriaxone may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms.
Animal studies have not demonstrated any teratogenic effects,however,there are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women.Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response,this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Ceftriaxone is excreted in breast milk in low concentration hence caution should be exercised when it is administered to a nursing woman.
Warnings and contraindications
Ceftriaxone should be used cautiously in patients sensitive to pencillin.
Ceftriaxone therapy should be discontinued in patients who develop signs or symptoms suggestive of gallbladder disease and conservative management considered.
Ceftriaxone is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the Cephalosporin group of drugs.
Administration
The injection is available in three strengths i.e.0.25g.0.5g.and 1.0g.Each strength can be injected either intramuscularly or intravenously.For intramuscular injection the diluting fluid is Lignocaine Hydrochloride 1% w/v solution I.P.and for intravenous injection the diluting fluid is Sterile WFI(water for injection).
The use of freshly prepared solution is recommended.
The dilution pattern to be followed is given below.
For intramuscular iniection:Cefaxone 0.25g or 0.5g is dissolved in 2 ml and Cefaxone 1 g in 3.5 ml of 1% w/v Lignocaine Hydrochloride solution I.P.and administered by deep intragluteal injection.It is recommended that not more than 1 g be injected on either side.The Lignocaine solution must never be administered intravenously.
For Intravenous injection:Cefaxone 0.25g or 0.5g is dissolved in 5 ml and Cefaxone 1gis dissolved in 10 ml of Sterile water for injection I.P.,and then administered by direct intravenous injection lasting 2-4 minutes.
Compatibility and stability
After reconstitution,protection from normal light is not necessary.The colour of solutions ranges from light Yellow to amber,depending on the length of storage,concentration and diluent used.
Cefaxone intramuscular solutions remain stable(loss of potency less than 10%)for the following time period.
Table 2

Cefaxone intravenous solutions at concentration of 10 mg/ml,20 mg/ml and 40 mg/ml remain stable for the following time periods stored in glass or PVC containers.
Table 3

Manufacturer
Lupin Laboratories Ltd.India