91.优维显
出处:按学科分类—医药、卫生 军事医学科学出版社《临床常用进口药物手册》第503页(26418字)
【中文释文】:
300/370(洛普酰胺)非离子型造影剂
〔成分〕
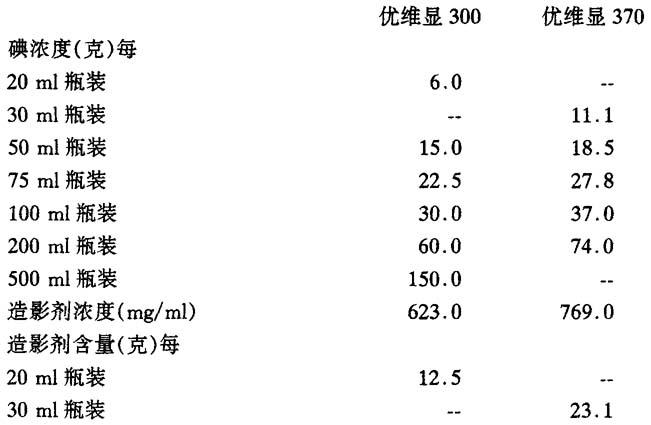
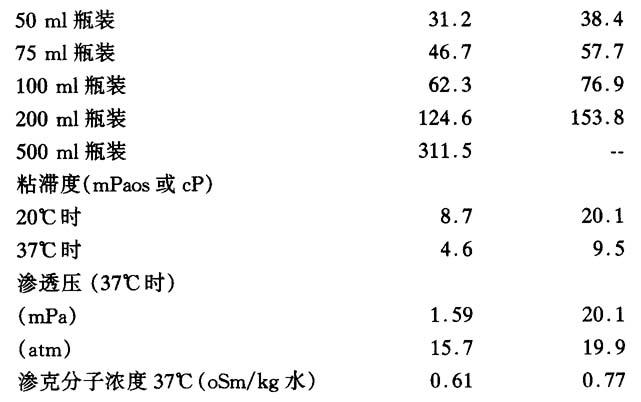
优维显300:每毫升水溶液含0.623g洛普酰胺
优维显370:每毫升水溶液含0.769g洛普酰胺
〔特性〕
优维显是一种低渗透压的非离子型造影剂,经肾排出,具有不同浓度的溶液,性质稳定,使用方便。其优点为:
全身耐受性优于离子造影剂;
优异的神经耐受性;
对心血管系统影响甚小;
内皮及内膜耐受性极佳;
无痛;
对血凝、纤溶系统和补体活性几乎无影响;
尿路显影对比度高;
以下适用于优维显370。
由于渗透压高,使用高碘浓度的非离子型造影剂时,对伴有剧痛的适应证(如外周动脉造影)亦应考虑造影剂所引起的血管性疼痛。
〔适应证〕

体腔造影(如关节造影、子宫输卵管造影、瘘管造影)但不能用于蛛网膜下腔造影,脑室造影或脑池造影。
〔剂量及给药方法〕
1.一般资料 非立即使用时,勿将造影剂吸入注射器或输液瓶。检查后剩余的造影剂必须废弃。瓶装造影剂并不是设计来多次穿刺使用,因此橡胶胶塞只能穿刺一次,最好使用18号以下的长针穿刺瓶塞(带侧孔的穿刺针如Nocore-Admix)最适合。
检查前病人需空腹,但须给予充分水分,纠正水和电解质失衡。此点尤适用于有电解质紊乱倾向的病人。
腹部血管造影和尿路造影时,肠内无异物及气体干扰,可提高诊断效果,病人在检查前2d起,禁食产气食品,特别是豌豆,黄豆,扁豆,沙拉,水果,新鲜面包和黑面包以及所有未煮过的蔬菜,检查前日,病人应于下午6时后禁食,也可在晚上使用泻药。
但婴儿、儿童及消瘦的病人,不应长时间禁食和使用泻药。
使病人镇静的措施和给予适当药物可使病人避免过度兴奋、不安和疼痛。这些因素可诱发副作用或加剧其副反应。
将造影剂加热至体温可增加耐受性。造影剂应尽可能在病人仰卧时注入。经验表明,给药后应继续观察病人至少30min,而严重的副作用大多发生在这段时间内。
非离子型造影剂的特性之一是对正常生理功能影响极微,因此在体外测试造影剂的抗凝血作用时,非离子型即低于离子型,所以造影剂和血液在注射器或导管中的接触时间越短越好。血管介入技巧要细致。并经常用生理盐水加肝素来清洗导管以减少可能引发血栓或栓塞的危险。
2.静脉肾尿路造影
(1)剂量
成人:如临床要求充分充盈输尿管,剂量应不少于1ml/kg体重优维显300(或0.8ml优维显370)。在特殊情况下,还可以适当增加剂量。
儿童:婴儿肾脏的肾单位尚未成熟,浓缩功能不足,需要较高剂量的造影剂。例如应采用优维显300:
新生儿:碘1.2g/kg,相当于4ml优维显300
婴儿:碘1.0g/kg,相当于4ml优维显300
幼儿:碘0.5g/kg,相当于1.5ml优维显300
(2)摄片时间:依上述剂量,注射优维显300/370需1~2min。一般肾实质在开始注射后3~5min内显影最佳,肾盂和尿路则在8~15min时显示最好。年轻病人应较早摄片,老年病人宜较晚摄片。
婴幼儿应提早于注射后2min摄第一片。
对比不佳应延迟摄片。
3.计算机体层(CT)增强
(1)头颅CT:以下剂量适用于头颅CT优维显300:最多2ml/kg。优维显370:最多1.5ml/kg。
(2)全身CT:全身CT的造影剂用量、注射速率依检查部位、诊断目的,尤其是所用扫描及重建影像的时间而异。使用低速扫描机宜行滴注,使用快速扫描机则应快速注射。
4.血管造影
用量视病人年龄,体重,心输出量,病人的健康状况,临床目的,被检查血管的性质和容量而不同。
参考剂量如下:
(1)脑血管造影
主动脉弓造影:50~80ml优维显300
逆行性颈动脉造影:30~40ml优维显300
选择性血管造影:6~15ml优维显300
(2)胸主动脉造影:50~80ml优维显300
(3)腹主动脉造影:40~60ml优维显300
(4)四肢血管造影
上肢:
动脉造影:8~12ml优维显300
静脉造影:15~30ml优维显300
下肢:
动脉造影:20~30ml优维显300
静脉造影:30~60ml优维显300
(5)心血管造影
特定心腔选择性造影:40~60ml优维显370
(6)冠状动脉造影:5~8ml优维显370
(7)数字减影血管造影(DSA)
根据使用离子型造影剂的经验,建议静脉“团注”注射30~60ml优维显300或优维显370(肘静脉流速8~12ml/s,腔静脉流速10~20ml/s)以清晰地显示大动脉、肺动脉,以及头部、颈部、肾及四肢动脉,然后,立即“团注”20~40ml生理盐水,以减少造影剂与血管壁的接触时间。
(8)动脉示DSA较传统的静脉法所需造影剂用量更少。选择性越高,造影剂用量越少。故肾功能损害者宜选用动脉法。与传统的血管造影比较,动脉法DSA所采用的造影剂浓度、用量及速率均可减少。
〔禁忌证〕
严重的甲状腺功能亢进。
妊娠及急性盆腔炎,禁行子宫输卵管造影。
〔注意事项〕
有碘造影剂过敏。严重的肝肾功能损害,心脏和循环功能不全,肺气肿,体质状况极差,重度脑动脉硬化,长期糖尿病,脑痉挛状态,潜在性甲状腺功能亢进,良性结节性甲状腺肿,多发性骨髓瘤等病人,需特别仔细地权衡检查的利弊。
经验表明,有过敏倾向的病人,较他人更易发生过敏反应。对这种病例,有些医师预防性地给予抗组胺药和(或)皮质类固醇。但造影剂与预防性药物不可混合注射。
孕妇使用优维显300/370是否安全,尚无定论,但妊娠期应尽量避免辐射,仔细权衡X线检查的利害得失。不论是否使用造影剂,嗜铬细胞瘤病人术前应给予α受体阻滞剂,以防止高血压危象。
注射经肾排泄的含碘造影剂后,甲状腺组织摄取诊断甲状腺异常的放射性同位素的能力降低可达2周,个别病例甚至更长。注射造影剂后,患糖尿病性肾病者使用造影剂可导致肾功能损害,可能加速服用双胍类药物病人的乳酸性酸中毒。为了病人的利益,双胍类药物应在造影剂检查前48h停止服用,并且等到肾功能恢复后才能重新服用。
〔副作用〕
静脉注射造影有关的副反应通常是轻微至中等程度而且是暂时的,但严重反应,甚至致命性的反应也曾被报告过。
恶心,呕吐,红斑,疼痛和温热感是最常见的反应。温热感或恶心感可以通过减慢注射速率,或暂停注射来改善。其它可能发生的症状是:寒颤,发热,出汗,头痛,晕眩,面色苍白,虚弱,窒息感,喘气,血压升高或降低,荨麻疹,各类皮疹,水肿,痉挛,发抖,喷嚏和流泪。这些反应可能是休克的先兆而与造影剂的用量及给药方式无关。这时,应立即停止注入造影剂,必要时,进行诊断性的静脉给药治疗。针管以选用软性插管为宜。以便紧急时,立即采取措施。检查室应配急救药,气管插管及呼吸器(参见造影剂意外时治疗建议)有过敏倾向的病人,更容易引发上述反应。
严重反应需要急救的情况可能有循环紊乱伴有外周血管舒张,血压下降,反射性心动过速,呼吸困难、激动、精神错乱、紫绀,以致于意识丧失,血管外注射造影剂很少导致严重的组织反应。
现已了解脑血管造影和其他会导致造影剂进入脑动脉的检查,可引发神经症状如昏迷,短暂性精神错乱和嗜眠症,一过性轻瘫,视力障碍,面肌松弛及癫痫发作,有癫痫病史或有脑损伤性癫痫的病人较易发作,罕见的情况下,也可由静脉内使用造影剂而诱发。
罕见短暂的肾功能衰竭。延迟反应偶尔发生。
〔造影剂意外的治疗建议〕
备妥急救药品和器械,熟悉急救措施对及时处理造影剂意外至关重要。建议采取以下措施:
1.静脉注射大剂量水溶性皮质类固醇,如6α-甲泼尼龙半琥珀酸钠,按下列剂量注射:
所有病例均立即静脉注射500mg(4岁以下250mg),于2~3min内注完,危重病人可追加剂量至30mg/kg体重(例如体重70kg者,大约注射2000mg),于3~5min内注完。
保留静脉插管或导管,维持血管通路。有些医师主张给予皮质类固醇之前应同时及早补充血容量(参阅“循环衰竭及休克”)。
2.给氧,必要时可正压给氧。进一步处理视病人情况及主要的症状而定。下列剂量仅适用于成人,儿童剂量依年龄酌减。
(1)循环衰竭和休克:立即置病人于休克位(头低,足臂高位),缓慢静脉注射周围血管加压药,注射血液代用品补充血容量。滴注去甲肾上腺素,将5mg溶于500ml溶液(如等渗盐水)中,剂量视效果而定,约10~20滴/min。连续监测脉率及血压。
(2)心脏停搏(心搏停止):快速、有力地叩击胸骨中段之胸壁,如无效,立即进行胸外心脏按压及人工呼吸(口对口,正压给氧,如可能行气管插管)。心内注射奥西那林(异丙喘宁)0.5mg。用心脏起搏器。当心脏恢复自主并有微弱的收缩后,静脉注射0.5~1g葡萄糖酸钙(10%溶液,5~10ml)。使用强心甙的病人慎用钙剂。
心室纤颤:立即进行胸外,心脏按压及人工呼吸,以除颤器除颤,如有必要可重复除颤。若无效或无除颤器,心内注射0.5g普鲁卡因胺。每5~10min静脉注射8.4%(即1mmol/ml)碳酸氢钠50ml,以拮抗在心室停搏或心室纤颤时产生的缺氧性酸中毒。检查血pH值。
(3)肺水肿:以血压计袖带阻断静脉,成人可切开静脉放血。静脉注射速效利尿剂,成人滴注40%葡萄糖溶液用于高渗利尿。如病人未洋地黄化,可给予适当的强心甙使其快速达到饱和量,例如成人给予毒毛花苷G0.125~0.25mg,静脉注射(二尖瓣狭窄病人慎用)。正压呼吸,但不能用于休克的病人。
(4)脑症状:病人烦躁,应肌肉或缓慢静脉注射镇定药如地西泮(安定),对严重的兴奋状态可加用异丙嗪50mg臀部注射。对脑器质性惊厥,肌肉注射0.2~0.4g苯巴比妥。严重的惊厥(癫痫持续状态),应静脉注射短效麻醉剂。
(5)过敏症状:
严重的荨麻疹:注射抗组胺药以加强皮质类固醇的作用,亦可予钙剂(使用强心甙者慎用);如哮喘发作,可非常缓慢地静脉注射氨茶碱制剂。如必要时可非常缓慢地静脉注射间奥那西林0.5mg;声门水肿者应缓慢地静脉注射抗组胺药(如异丙嗪50mg);如发生上呼吸道梗阻,可考虑气管切开。
〔包装〕
优维显300: 20ml瓶装
50ml瓶装
75ml瓶装
100ml瓶装
500ml瓶装
优维显370: 30ml瓶装
50ml瓶装
75ml瓶装
100ml瓶装
200ml瓶装
将所有药品妥为存储,勿使儿童拿到。
〔生产厂家〕
德国先灵公司
【外文释文】:
Non-ionic contrast medium
Composition
Ultravist 300:1 ml contains 0.623 g lopromide
Ultravist 370:1 ml contains 0.769 g lopromide
in aqueous solution
ultravist 300 Ultravist 370

Properties
Ultravist is a non-ionic,renal contrast medium with low osmotic pressure which is available as stable,ready-to-use solutions of different concentrations.
Its advantages are:
·Better general tolerance compared to ionic contrast media
·Excellent neural tolerance
·Little influence on the cardiovascular system
·Very good endothelial and intimal tolerance
·Virtually painless administration
·Little influence on clotting,fibrinolysis and complement activation
·High contrast density in the urinary tract.
*The following applies to Ultravist 370:
In indications attended by intensive pain(e.g.peripheral arteriography)vascular pain has to be reckoned with also on administration of non-ionic contrast media of high iodine concentration because of their high osmolality.
Indications
1.Ultravist 300
Contrast enhancement in computerized tomography(CT),digital subtraction angiography(DSA),intravenous urography,phlebography of the extremities,venography,arteriography,visualization of body cavities(e,g.arthrography,hysterosalpingograhy,fistulography)with the exception of myelography,ventriculography and cisternography.
2.Uitravist 370
Contrast enhancement in computerized tomography(CT),digital subtraction angiography(DSA),intravenous urography,arteriography and especially angiocardiography,visualization of body cavities(e,g.arthrography,fistulography)with the exception of myelography,ventric ulography and cisternography.
Dosage and administration
1.General information
The contrast medium solution should not be drawn into the syringe or the infusion bottle attached to the infusion set until immediately before the examination.
Vials containing contrast medium solutions are not intended for the withdrawal of multiple doses,The rubber stopper should never be pierced more than once.The use of cannulas with a long tip and a maximum diameter of 18G is recommended for piercing the stopper an drawing up the contrast medium(dedicated withdrawal cannulas with a side hole,e.g.Nocore-Admix cannulas are particularly suitable).
Contrast medium solution not used in one examination session must be discarded.
The patient should attend for examination fasting but adequately hydrated.Disorders of the water and electrolyte balance must be corrected.This applies in particular to patients who are predisposed to such disturbances.In the case of abdominal angiography and urography,the diagnostic yield is increased if the bowels are emptied of faecal matter and gas.On the two days prior to the examination,patients should therefore avoid flatulent food,in particular peas,beans and lentils,salads,fruits,dark and fresh bread and all kinds of uncooked vegetables.On the day before the examination,patients should refrain from eating after 6 p.m.Moreover,it can be appropriate to administer a laxative in the evening.
In babies,young children and marantic patients,however,prolonged fasting and the administration of a laxative before the examination are contraindicated.
Experience shows that pronounced states of excitement,anxiety and pain can be the cause of side effects or intensify contrast medium-related reactions.They can be counteracted by calm management of the patient and the use of suitable drugs.
Experience shows that contrast medium is tolerated better if it is warmed to body temperature.
Intravascular administration of contrast media should,if possible,be done with the patient lying down.After the administration,the patient should be kept under observation for at least 30 minutes,since experience shows that the majority of all severe incidents occur within this time.
A property of non-ionic contrast media is the extremely low interference with normal physiological functions.As a consequence of this,non-ionic contrast media have less anticoagulant activity in vitro than ionic contrast media.therefore,The period of contact between blood and contrast media in syringes and catheters should be kept as short as possible and meticulous attention should be paid to the angiographic technique and frequent catheter flushing with physiological saline solution(if necessary with heparin added)so as to minimize the risk of procedure-related thrombosis and embolism.
2.Intravenous urography
(1)Dosage
Adults:the dose should not be less than 1 ml Uhravist 300(0.8 ml Ultravist 370)per kg body weight if the clinical problem also requires filling of the ureters.Increasing the dose is possible if this is considered necessary in special indications.
Children:the physiologically poor concentrating ability of the still immature nephron of infantile kidneys demands relatively high doses of contrast medium,e.g.with the use of Ultravist300:
Neonates:1.2 g l/kg body weight,corresponding to about 4.0 ml/kg body weight.
Babies:1.0 g I/kg body weight,corresponding to about 3.0 ml/kg body weight.
Small children:0.5g I/kg body weight,corresponding to about 1.5 ml/kg body weight.
(2)Filming times
When the above dosage guidlines are observed and Ultravist 300/370 is injected over 1 to 2 minutes,the renal parenchyma is usually highly opacified 3 to 5 minutes and the renal pelvis with the urinary tract 8 to 15 minutes after the start of administration.The earlier time should be chosen for younger patients and the later time for older patients.In babies and young children it is advisable to take the first film as early as about 2 minutes after the administration of the contrast medium.Insufficient contrast can necessitate later films.
3.Computerized tomography(CT)
(1)Cranial CT
The following dosages are recommended for cranial CT:
Ultravist 300:1-max.2 ml/kg body weight
Ultravist 370:1-max.1.5 ml/kg body weight
(2)Whole-body CT
In whole-body computerized tomography,the necessary doses of contrast medium and the rate of administration depend on the organs under investigation,the diagnostic problem and,in particular,the different scan and image reconstruction times of the scanners in use.The infusion should be preferred for slow scanners and the injection as a bolus for fast scanners.
4.Angiography
The dosage depends on the age,weight,cardiac output and general condition of the patient,the clinical problem,examination technique and the nature and volume of the vascular region to be investigated.
Sugested dosages:
(1)Cerebral angiography
Aortic arch angiography 50-80 ml Ultravist 300
Retrograde carotid angiography 30-40 ml Ultravist 300
Selective angiography 6-15 ml Ultravist 300
(2)Thoracic aortography 50-80 ml Ultravist 300
(3)Abdominal aortography 40-60 ml Ultravist 300
(4)Angiography of the extremities
Upper extremities:
Arteriography 8-12 ml Ultravist 300
Venography 15-30 ml Ultravist 300
Lower extremites:
Arteriography 20-30 ml Ultravist 300
Venography 30-60 ml Ultravist 300
(5)Angiocardiography
Selective,in the individual
cardiac cavities: 40-60 ml Ultravist 370
(6)Coronarangiography 5-8 ml Ultravist 370
(7)Digital subtraction angiography(iv DSA)
Basing on experience with ionic contrast media,the iv injection of 30-60 ml Ultravist 300 or 370 as a bolus(flow rate:8-12 ml/s into the cubital vein;10-20 ml/s into the vena. cava)is recommended for high contrast demonstrations of the great vessels,of the pulmonary arteries and of the arteries of the neck,head,kidneys and extremities.The period of time for which the contrast medium is in contact with the wall of the veins can be reduced by injecting 20 to 40 ml isotonic sodium chloride solution as a bolus immediately afterwards.
(8)Intraarterial digital subtraction angiography(ia DSA)
Intraarterial digital subtraction angiography requires smaller volumes and lower iodine concentrations than the intravenous technique.The more selective the angiography is,the lower the dose of contrast medium can be.This method is therefore recommended for patients with impaired renal function.The values used in conventional angiography for bolus concentration,bolus volume and flow rate can be reduced for intraarterial DSA.
Contraindications
Manifest hyperthyroidism.
Hysterosalpingography must not be performed during pregnancy or in the presence of acute inflammatory processes in the pelvic cavity.
Please note
The need for examination requires particularly careful consideration in hypersensitivity to iodinated contrast media,severe impairment of hepatic or renal function,cardiac and circulatory insufficiency,pulmonary emphysema,very poor general condition,advanced cerebral arteriosclerosis,diabetes mellitus requiring treatment,cerebral spasmodic conditions,latent hyperthyroidism,bland nodular goitre and multiple myeloma.
Experience shows that patients with an allergic disposition suffer more frequently than others from hypersensitivity reactions,In such cases,some examiners administer e.g.antihistamines and/or corticoids prophylactically.However,contrast media and prophylactic agents should not be mixed and injected together.
In patients with multiple myeloma,diabetes mellitus requiring treatment,polyuria,oliguria or gout and in babies,small children and patients in a very poor general state of health,fluid intake should not be restricted even before the use of iso-osmolar contrast media.
It has not yet been demonstrated that Ultravist 300 is safe for use in pregnant patients.Since.where possible,radiation stress should in any case be avoided during pregnancy,the benefits of any X-ray examination-whether with or without contrast material should for this reason alone be carefully weighed against the possible risk.
Premedication with alpha-receptor blockers is recommended in phaeochromocytoma patients because of the risk of blood pressure crise.
Following the administration of iodinated renal contrast media,the capacity of the thyroid tissue to take up radioisotopes for diagnosing disorders of the thyroid is reduced for up to 2 weeks,and even longer in individual cases.
Diabetic nephropathy may predispose to renal impairment following intravascular contrast medium administration.This may precipitate lactic acidosis in patients who are taking biguanides.As a precaution,biguanides should be stopped 48 hours prior to the contrast medium examination and reinstated only after adequate renal function has been regained.
Side effects
Side effects in association with the intravascular use of iodinated contrast media are usually of a mild to moderate and temporary nature.However,nausea,vomiting,erythema,a sensation of pain and a general feeling of warmth are the most frequently recorded reactions on intravascular administration.Subjective complaints such as sensations of warmth or nausea can usually be alleviated quickly by reducing the rate of administration or interrupting the administration briefly.
Other symptoms which may occur are:chills,fever,sweating,headache,dizziness,blanching,weakness,gagging and a feeling of suffocation,gasping,a rise or fall of blood pressure,itching,urticaria,other kinds of skin eruption,oedema,cramp,tremor,sneezing and lacrimation.These reactions,which can occur irrespective of the amount administered and the mode of administration,may be the first signs of incipient state of shock.Administration of the contrast medium must be discontinued immediately and if necessary,specific therapy instituted via a venous access.It is therefore advisable to use a flexible indwelling cannula for intravenous contrast medium administration.To permit immediate counter measure to be taken in emergencies,appropriate drugs,an endotracheal tube and a ventilator should be ready to hand(cf.”Suggestions for the treatment of contrast medium incidents”).Experience shows that hypersensitivity reactions occur more frequently in patients with an allergic disposition.
Severe reactions requiring emergency treatment can occur in the form of a circulatory reaction accompanied by peripheral vasodilatation and subsequent hypotension,reflex tachycardia,dyspnoea,agitation,confusion and cyanosis and possible leading to unconsciousness.
Paravascular administration of the contrast medium rarely leads to severe tissue reactions.
It is known that cerebral angiography and other procedures in which the contrast medium reaches the brain with the arterial blood can be accompanied by neurological complications such as coma,temporary states of confusion and somnolence,transient pareses,disturbed vision or slack facial muscles and particularly in epileptics and patients with focal brain damageepileptic fits.Very rarely,the induction of fits in these patients has been described on intravenous administration of the contrast medium as well.
Temporary renal failure may occur in rare cases.Delayed reactions can occasionally occur.
Suggestions for the treatment of contrast medium incidents
It is of decisive importance for prompt action in the event of contrast medium incidents to have all drugs and instruments for emergency therapy readily available and to be familiar with the practice of emergency measures.
The following procedure is recommended:
1.Intravenous injection of a high-dosed water-soluble corticoid,e.g.6α-methylprednisolone-hemisuccinate sodium at the following dosage:
·In all cases immediately 500 mg(children under 4 years 250 mg)over a period of 2 to 3 minutes;
·In life-threatening conditions increase the dose over a period of another 3-5 minutes to 30 mg/kg body weight(example:approx.2 000 mg for 70 kg body weight).
Leave the cannula or catheter in the vein to maintain access to the vascular system.Some doctors prefer early volume replacement(cf.“Circulatory insufficiency and shock”)and implement this before or when administering the corticoid.
2.Administer oxygen,if necessary carry out positive-pressure oxygen respiration.
Further measures will depend on the most prominent symptoms and the condition of the patient.The dosages of the specified preparations are valid only for adults and must be reduced for children in accordance with their age.
(1)Circulatory insufficiency and shock:immediately place the patient in the shock position(head down,legs and arms high).Slow iv injection of peripheral vasopressors,volume replacement with blood substitutes.Infuse noradrenaline,5 mg in 500 ml liquid(e.g.isotonic sodium chloride solution),dosage according to effect,about 10-20 drops/minute.Continuously check pulse and blood pressure.
(2)Cardiac arrest(asystole):energetic,quickly slackening pressure on the thoracic wall over the middle of the sternum;if unsuccessful,immediately extrathoracic cardiac massage and artificial respiration(mouth to mouth,positive-pressure oxygen respiration,where possible endotracheal intubation),0.5mg orciprenaline intracardially,cardiac pacemaker.After the return of spontaneous but weak cardiac contractions calcium gluconate 0.5-1 g.iv(5-l0ml of a 10%solution).Beware of using calcium in patients receiving cardiac glycosides.
Ventricular fibrillation:immediately extrathoracic cardiac massage and artificial respiration.Defibrillation with a cardiac defibrillator,repeat if necessary.If unsuccessful or no defibrillator is available,procainamide 0.5 g intracardially.Sodium bicarbonate solution iv,e.g.50 ml of an 8.4%solution(1 mmol/ml)every 5-10 minutes,to combat the hypoxaemic acidosis which always develops in the event of cardiac arrest or ventricular fibrillation.
(3)Pulmonary oedema:phlebostasis with a blood pressure cuff,in adults perhaps phlebotomy.A quick-acting diuretic iv and,in adults infusion of 100 ml of a 40%glucose solution for osmodiuresis.If patient is not yet digitalized,rapid saturation with a suitable cardiac glycoside,e.g.in adults 0.125-0.25 mg ouabain(strophanthin)iv(beware in cases of mitral stenosis).Positive-pressure respiration,but not in patients with shock.
(4)Cerebral symptoms:in the event of restlessness a tranquillizer(e.g.diazepam)im or slowly iv;in severe states of excitation neuroleptics,possibly combinedwith promethazine 50 mg,intragluteally.For cerebroorganic convulsions phenobarbital 0.2-0.4 g im,for severe convulpive states(epileptic status)iv injection of a short-acting anaesthetic.
(5)Allergic symtoms:for severe urticaria,injection of an antihistamine,possibly also a calcium preparation,in addition to corticoids(caution must be exercised with calcium in patients receiving cardiac glycosides);for asthmatic attacks a theophylline preparation very slowly iv,if necessary orciprenaline 0.5 mg very slowly iv in oedema of the glottis an antihistamine(e.g.promethazine 50mg)slowly iv.Tracheotomy may be necessary if the upper respiratory tract is obstructed.
Presentation
Ultravist 300: Ultravist 370:
Vials of 20 ml Vials of 30 ml
Bottles of 50 ml Bottles of 50 ml
Bottles of 75 ml Bottles of 75 ml
Bottles of 100 ml Bottles of 100 ml
Bottles of 200 ml Bottles of 200 ml
Bottles of 500 ml
Some presentations may not be available temporarily.
Store all drugs properly and keep them out of reach of children.
Manufacturer
Schering AG,Germany